Balanced Scorecard |
Robert S. Kaplan & David P. Norton |
| Recommend this article to your friends! |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
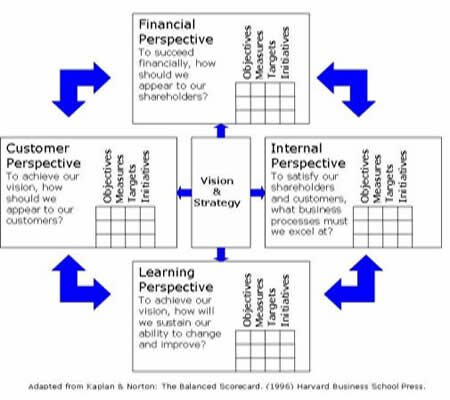
The theory behind the Balanced Scorecard was developed by Robert S. Kaplan & David P. Norton. The aim of the Balanced Scorecard is to clarify and communicate a company's vision and strategy into action. The balanced scorecard framework is founded on four perspectives, the four perspectives are:
1. Financial perspective,
2. Customer perspective,
3. Business process perspective,
4. Learning and growth perspective.
Below, the four perspectives are shortly described. The measures suggested below are not suited for every company, and measures should be chosen by the respective company only after careful consideration, so that each measure can evaluate and control the success of the company's strategy implementation.
The financial perspective The financial perspective entails the use of traditional financial measures that try to examine, whether or not the company's strategy is contributing to the bottom-line improvement of the company. The financial perspective is therefore trying to evaluate the results obtained from the strategy, and is trying to capture the strategy's success in traditional financial terms. The selection of financial measures will most likely be inspired by the life cycle stage of the products or services being supplied by the company. The three possible stages, as described by Kaplan and Norton (1996), are rapid growth, sustain, and harvest. For the growth stage, companies will probably use measures that can evaluate the growth and development of the company. Such financial measures could be: increased sales volumes, acquisition of new customers, growth in revenues etc. Financial measures in the sustain stage will probably be characterized by measures that can evaluate the effectiveness of the organization. Financial measures in this stage could be: return on investment (ROI), the return on capital employed, etc. Finally, the harvest stage will potentially be based on different cash flow analysis that try to evaluate the company's success in harvesting profits from aging products or services. Measures in this stage could be: payback periods and revenue volume.
Popular measures: Cash flow Return on investment Financial result Return on capital employed Return on equity Residual income Economic Value Added
The customer perspective The aim of the customer perspective is to define the value proposition of the company. The company will try to define the value it wants to apply to the end-user that will potentially satisfy the customer's needs. Measures that are selected for the customer perspective should measure the quality and perceived value of the products or services, that are supplied to the customer. Measures in this perspective may be delivery times, innovation, quality, performance, service, costs etc. Likewise, measures in the customer perspective should also try to evaluate the results of the value proposition such as: customer satisfaction, customer retention etc.
Popular measures: Time-to-market Service Innovation Technological excellence Costs Customer satisfaction Customer retention
The internal process perspective The internal process perspective is concerned with the internal processes within a company that create and deliver the goods and services of the company. It is also concerned with the processes that are to deliver the value proposition defined in the customer perspective. It focuses on the activities and key processes required in order for the company to excel at providing the value expected by the customers, so that the measures in the customer perspective will be supported. Measures in this perspective could also be implemented to support the measures in the financial perspectives, where e.g. smaller lead-times or better quality may result in greater profits. Measures in the internal perspective could be: lead-time, innovation rates, service measures, quality measures, efficiency measures, costs reductions etc.
Popular measures: Efficiency measures Cost reductions Service handling measures Innovation rates Lead time measures Time to market
The innovation and learning perspective The innovation and learning perspective is the foundation of any strategy and focuses on the human and intangible assets of the company. This focus is mainly on the internal skills and capabilities that are required to support the value-creating internal processes. This perspective tries to define the human and developmental requirements of the company that will enable ambitious objectives in the other three perspectives to be achieved.
Popular measures: Illness rates Employee turnover Education and development
The strategy formulation process of a company will most likely stem from the financial perspective, where the measures in the remaining perspectives will be structured to enable and support the financial goals of the company and its stakeholders.
The image below shows an example of a balanced scorecard, where measures, goals and initiatives in each perspective are compiled in a scorecard. |
| Date Created: 2009-09-07 |
| Posted by: Admin |
 |
|
Related resources: |
| What is Michael Porter's 5 forces? Internationalization of Multinational Corporations Global strategies for MNCs: Christopher A. Bartlett & Sumantra Ghoshal What is the PESTEL Framework? What is the BCG Matrix? |
| Reference(s) |
| The Balanced Scorecard: Translating Strategy into Action |
| Kaplan, Robert S. & Norton, David P.; (1996); Harvard Business School Press |
| Keywords: |
Online MBA, Online MBA Courses, Robert S. Kaplan, David P. Norton, Balanced Scorecard, BSC, financial perspective, customer perspective, internal process perspective, innovation and learning perspective |
Copyright © BusinessMate 2009-2014
